At Advanced Prototype Molding, our four decades of experience enable us to provide our customers with expertly crafted prototypes and a one-stop shopping experience. We provide a range of rapid prototyping techniques. This method of fabrication utilizes 3D computer-aided designs (CAD) to create scale model prototypes at speeds that were formerly impossible. As such, rapid prototyping is an indispensable process in a range of industries.
Rapid prototyping is an umbrella term for a range of processes and techniques that enable manufacturers to quickly fabricate accurate scale models of a product or part. Every technique offers its own benefits depending on the unique needs of the project. Regardless of the specific method used, rapid prototyping will utilize CAD data to create the final prototype.
The use of CAD data drastically speeds up the production process, which is more important than ever in fast-paced modern markets. For many businesses, success depends on an ability to quickly develop new products to stay competitive. Rapid prototyping assists in this development, helping companies continually introduce high-quality products.
When creating prototypes, there are two types a company might choose:
Depending on the desired style of prototype, a manufacturer may utilize a range of different prototyping techniques. Three of the most common methods of production are additive manufacturing, CNC machine prototyping, and quick-turn tooling. Urethane molding is another rapid prototyping technique that produces products with soft rubber parts in low production volumes. Urethane-molded prototypes can feature simple or complex designs and come in various sizes and colors to meet your needs.
This type of manufacturing is both straightforward and cost-efficient, making it the most popular option. Additive manufacturing offers high amounts of flexibility, as it consists of creating a prototype by continually adding layers of substrate until the model is complete. Manufacturers can easily add or remove features of the prototype during the production process.
There are several significant subtypes of additive manufacturing, including stereolithography and selective laser sintering. Stereolithography is ideal for creating complex, intricate parts. It also offers an aesthetic advantage, producing parts with excellent surface finishes. Selective laser sintering creates products by utilizing a laser to fuse a nylon-based powder. Prototypes made using this method are highly durable during testing.
Regardless of the specific process used, prototypes created through rapid prototyping have applications in a wide range of industries, including:
Computer numerical control (CNC) machining fabricates prototypes through a cutting and milling process that is controlled by computers. The use of computers provides high levels of dimensional accuracy.
Quick-turn tooling enables the rapid production of tooling for injection molded parts. With these capabilities, manufacturers can produce aluminum tooling for short-run prototypes in a wide range of plastic and elastomeric injection molding materials. The benefits of quick-turn tooling include fast lead times, precision, and cost-effectiveness.
Urethane molding or casting is another method of quick-turn tooling. Permanent production tooling is often made from durable materials like steel; however, this tooling can take weeks to manufacture. For projects where longer lead times can be an issue, urethane molded parts enable manufacturers to start production to meet demands until the permanent tooling is ready.
Rapid prototyping offers many advantages in addition to its impressive manufacturing speed.
Expensive custom tooling is not required for rapid prototyping, as this process utilizes CAD models. As such, designers have greater freedom to experiment and adjust different aspects of the prototype without the continual expense of new tooling. This further speeds up the prototyping process and makes it significantly easier to fabricate an effective final product.
Without the ability to test a physical prototype, it is challenging for engineers to identify potential problems in the product. This can result in flaws that are only identified after the final product has been manufactured. With a prototype, however, engineers and designers can catch these flaws and optimize the product before its production run, thus saving a significant amount of time and money.
Whether team members are talking with each other or with their customers, a prototype serves as a highly beneficial communication tool. Explaining a design concept without the use of a prototype forces the speaker to depend on abstract ideas that are prone to misinterpretation. With a physical model of the final product, however, designers and customers can communicate their ideas more clearly and easily throughout the design process.
For over 40 years, Advanced Prototype Molding has been working closely with our customers to fabricate high-quality prototypes. Our capabilities include stereolithography and selective laser sintering, as well as options such as fused deposition modeling and direct metal laser sintering. With a wide array of services under one roof, we provide our customers with an efficient and reliable production experience. To learn more about how we can assist with your prototyping needs, contact us or request your quote today.
Click to Enlarge
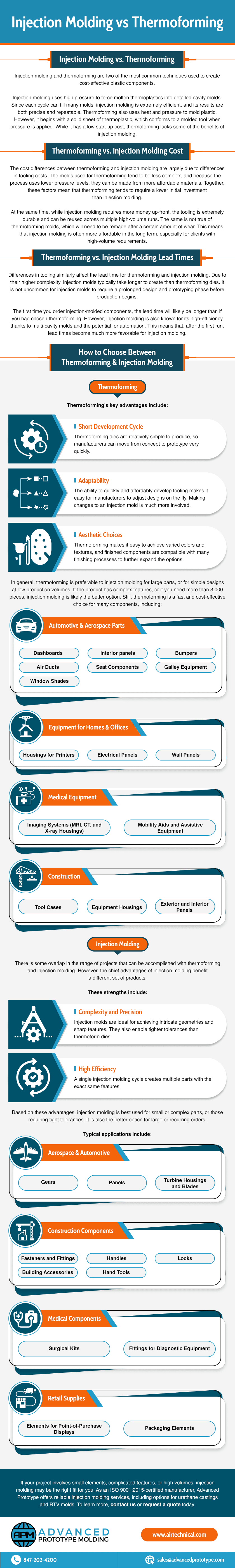
Injection molding and thermoforming are two of the most common techniques used to create cost-effective plastic components.
Injection molding uses high pressure to force molten thermoplastics into detailed cavity molds. Since each cycle can fill many molds, injection molding is extremely efficient, and its results are both precise and repeatable. Thermoforming also uses heat and pressure to mold plastic. However, it begins with a solid sheet of thermoplastic, which conforms to a molded tool when pressure is applied. While it has a low start-up cost, thermoforming lacks some of the benefits of injection molding.
This article explores the advantages of each process to help you make the optimal choice for your next thermoplastics project.
The cost differences between thermoforming and injection molding are largely due to differences in tooling costs. The molds used for thermoforming tend to be less complex, and because the process uses lower pressure levels, they can be made from more affordable materials. Together, these factors mean that thermoforming tend to require a lower initial investment than injection molding.
At the same time, while injection molding requires more money up-front, the tooling is extremely durable and can be reused across multiple high-volume runs. The same is not true of thermoforming molds, which will need to be remade after a certain amount of wear. This means that injection molding is often more affordable in the long term, especially for clients with high-volume requirements.
Differences in tooling similarly affect the lead time for thermoforming and injection molding. Due to their higher complexity, injection molds typically take longer to create than thermoforming dies. It is not uncommon for injection molds to require a prolonged design and prototyping phase before production begins.
The first time you order injection-molded components, the lead time will likely be longer than if you had chosen thermoforming. However, injection molding is also known for its high-efficiency thanks to multi-cavity molds and the potential for automation. This means that, after the first run, lead times become much more favorable for injection molding.
When considering injection molding vs. thermoforming, it is important to consider how the methods' advantages relate to your project parameters.
Thermoforming's key advantages include:
In general, thermoforming is preferable to injection molding for large parts, or for simple designs at low production volumes. If the product has complex features, or if you need more than 3,000 pieces, injection molding is likely the better option. Still, thermoforming is a fast and cost-effective choice for many components, including:
There is some overlap in the range of projects that can be accomplished with thermoforming and injection molding. However, the chief advantages of injection molding benefit a different set of products. These strengths include:
Based on these advantages, injection molding is best used for small or complex parts, or those requiring tight tolerances. It is also the better option for large or recurring orders. Typical applications include:
Injection molding and thermoforming are both effective, versatile techniques with many advantages. There is no single best choice that suits all projects. Instead, you should consider project parameters and constraints to identify the best option.
If your project involves small elements, complicated features, or high volumes, injection molding may be the right fit for you. As an ISO 9001:2015-certified manufacturer, Advanced Prototype offers reliable injection molding services, including options for urethane castings and RTV molds. To learn more, contact us or request a quote today.
Manufacturers use molding processes to create high-volume orders of precision components, prototypes, and everything in between. There are multiple different types of molding processes available, with blow molding and injection molding being popular options. Both can create high-quality parts that meet tight tolerances and budget requirements. However, there are key differences between the two processes that are important to understand before selecting the right fit for your next production order.
Click to Enlarge
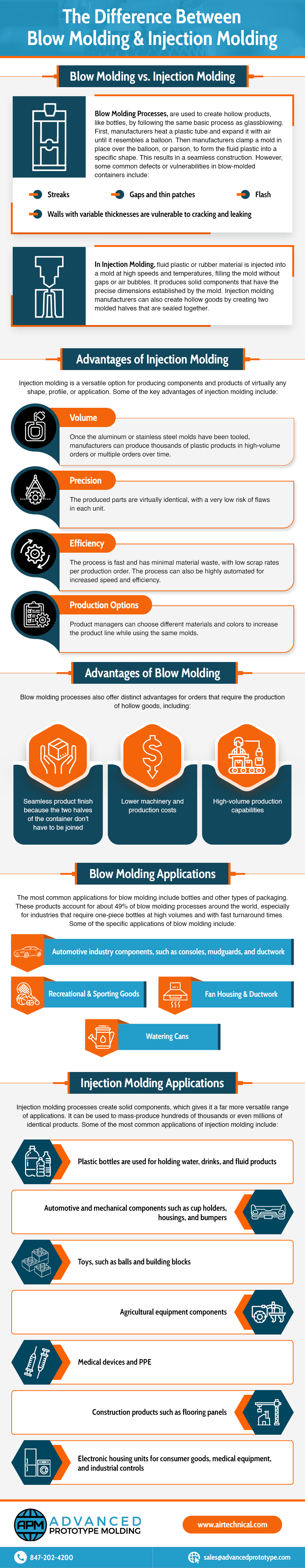
Ultimately, blow molding and injection molding are used to create different types of products. In injection molding, fluid plastic or rubber material is injected into a mold at high speeds and temperatures, filling the mold without gaps or air bubbles. It produces solid components that have the precise dimensions established by the mold. Injection molding manufacturers can also create hollow goods by creating two molded halves that are sealed together.
Blow molding processes, on the other hand, are used to create hollow products, like bottles, by following the same basic process as glassblowing. First, manufacturers heat a plastic tube and expand it with air until it resembles a balloon. Then manufacturers clamp a mold in place over the balloon, or parson, to form the fluid plastic into a specific shape. This results in a seamless construction. However, some common defects or vulnerabilities in blow-molded containers include:
While both processes are cost-effective and reliable, the type of product you want to produce is the main deciding factor in which process you should select.
Injection molding is a versatile option for producing components and products of virtually any shape, profile, or application. Some of the key advantages of injection molding include:
Blow molding processes also offer distinct advantages for orders that require the production of hollow goods, including:
Both blow molding and injection molding can quickly and efficiently produce plastic goods. But injection molding is commonly used to create solid plastic parts and products with a filled interior, and blow molding creates seamless, hollow parts, such as bottles and hollow toys. Because the two processes produce different types of plastic goods, the applications for each method differ.
The most common applications for blow molding include bottles and other types of packaging. These products account for about 49% of blow molding processes around the world, especially for industries that require one-piece bottles at high volumes and with fast turnaround times. Some of the specific applications of blow molding include:
Injection molding processes create solid components, which gives it a far more versatile range of applications. It can be used to mass-produce hundreds of thousands or even millions of identical products. Some of the most common applications of injection molding include:
Both injection molding and blow molding processes are popularly used throughout multiple different industries. At Advanced Prototype Molding, we're a leading provider of high-quality plastic molding, mold fabrication, plastic finishing services, and more. Contact us today to learn more about our capabilities or request a quote for pricing details.
In the world of manufacturing, prototypes are commonly used in both the design and development of physical objects, particularly when large system building construction or manufacturing is involved. Advanced Prototype Molding has over 40 years of experience in building reliable, high-quality prototypes. Here, we will discuss the importance of product prototyping as well as its processes, materials, and benefits.

Prototyping is a process in which a sample product is created that can then be tested in a “real world” environment similar to the one the final product will be used in. It gives you a chance to test quality and identify issues in a relatively low-stakes environment before mass production begins. A prototype serves as a "throwaway" model that is made to understand the requirements of a project prior to the design and coding phases.
Rapid prototyping is an accelerated version of prototyping that employs both 3D CAD software and 3D printing technology. With a rapid prototype, customized products no longer need to be created from scratch - thus improving product development significantly.
For projects that require revision and end-user feedback, prototyping is a must. It's far easier and less expensive to implement significant changes on a prototype than it is once a product has entered full-scale production. By creating a prototype, you can actually physically interact with a proposed product and see which elements of it are working and, more importantly, which ones need refining.
There are various prototype manufacturing processes to choose from depending on your needs. These include:

At Advanced Prototype Molding, we offer these product prototyping methods with a wide range of material options, including:
Plastics:
Rubber:
Metals:
Misc:
Advanced Prototype Molding can help you select the best prototyping method and materials for your specific application.
Prototype manufacturing brings with it a wide range of benefits. One of its main advantages is its ability to reduce time and costs. Prototyping allows you to address small problems now before they have a chance to become much bigger ones later on in the manufacturing process, thus increasing the speed at which you're able to get your products to market.

Not only that, but the prototyping process allows you to better test product features, manufacturing methods, user experiences, and more before you enter full-scale production. Product prototyping also leads to better visualization of the final product as well as improved and increased user involvement.
Product prototyping offers a host of advantages that make it an extremely important manufacturing process for various industries. By being able to test and visualize the product, you can make the necessary adjustments and improvements before final production, saving both time and money.
At Advanced Prototype Molding, we offer a broad selection of rapid prototyping and 3D printing services for various industries, including:
If you'd like to find out more information about the benefits of product prototyping, or for more information about our services, please contact Advanced Prototype Molding today. You can also fill out a request for quote to get started on your next rapid prototyping project.
Injection molding and 3D printing have many similarities since both processes take an abstract design and turn it into a 3D object. However, while they often seek to accomplish the same or similar goals, they also have distinct characteristics that make them appropriate for different prototyping and production projects. For example, 3D printing is an additive process that is suitable for low-volume runs, while injection molding is a shaping process that is better suited for high-volume runs. Understanding the differences between the two is key to choosing the best method for your needs.
3D printing utilizes a specialized printer and filament material to create the desired object from a digital design file. The printer builds the object by adding successive layers of filament as per the specifications outlined in the file.
Injection molding utilizes pre-made molds to shape material into the desired object. The process involves heating the material to a molten state and then injecting it at high pressures into the mold. After a cooling period, the material is able to maintain the shape of the mold, at which point it is removed and sent for further processing if needed.

Click to Enlarge
While both injection molding and 3D printing can be used for prototyping and production operations, their suitability for a particular project depends on the part and production specifications.
As an additive manufacturing process, 3D printing does not require the use of a mold. Eliminating this tooling requirement benefits manufacturers in many ways. For example:
Given the above, 3D printing is commonly used during the prototyping phase for new parts and products.
One thing to keep in mind regarding 3D printing is that the maximum size of the printed component is limited by the capacity of the print bed. As a result, 3D printed parts and products are generally to under 30”.
As injection molding operations require the use of molds, they generally have longer turnaround times than 3D printing operations since manufacturers need to wait for the mold to be created and delivered. This tooling requirement increases the overall cost of injection molding operations and makes it harder to accommodate design changes. That’s why manufacturers generally use the process for projects involving high production quantities since it lowers per-unit tooling costs.
One thing to keep in mind regarding injection molding is that it can accommodate designs of nearly any size or complexity. Additionally, the molds can be constructed to create multiple units of the same component or different components simultaneously. This capability helps reduce the overall manufacturing time for an order.
Need assistance choosing between 3D printing and injection molding for your next project? Ask the experts at Advanced Prototype Molding! Equipped with over 40 years of experiencing building prototypes and turning them into fully-fledged components, our team has the knowledge and skills to help you determine the right production method for your unique application. Additionally, whether you settle on 3D printing or injection molding, we’re ready to bring your idea to life.
To learn more about our 3D printing and injection molding capabilities, check out our 3D printing and injection molding services pages or contact us today. To discuss your project specifications with one of our team members, request a quote.



ADVANCED PROTOTYPE MOLDING
1520 N Old Rand Road Wauconda, IL 60084
Tel: 847-202-4200
Fax: 847-202-4270
sales@advancedprototype.com

ADVANCED PROTOTYPE MOLDING
1520 N Old Rand Road Wauconda, IL 60084
Tel: 847-202-4200
Fax: 847-202-4270
sales@advancedprototype.com