Injection molding and 3D printing have many similarities since both processes take an abstract design and turn it into a 3D object. However, while they often seek to accomplish the same or similar goals, they also have distinct characteristics that make them appropriate for different prototyping and production projects. For example, 3D printing is an additive process that is suitable for low-volume runs, while injection molding is a shaping process that is better suited for high-volume runs. Understanding the differences between the two is key to choosing the best method for your needs.
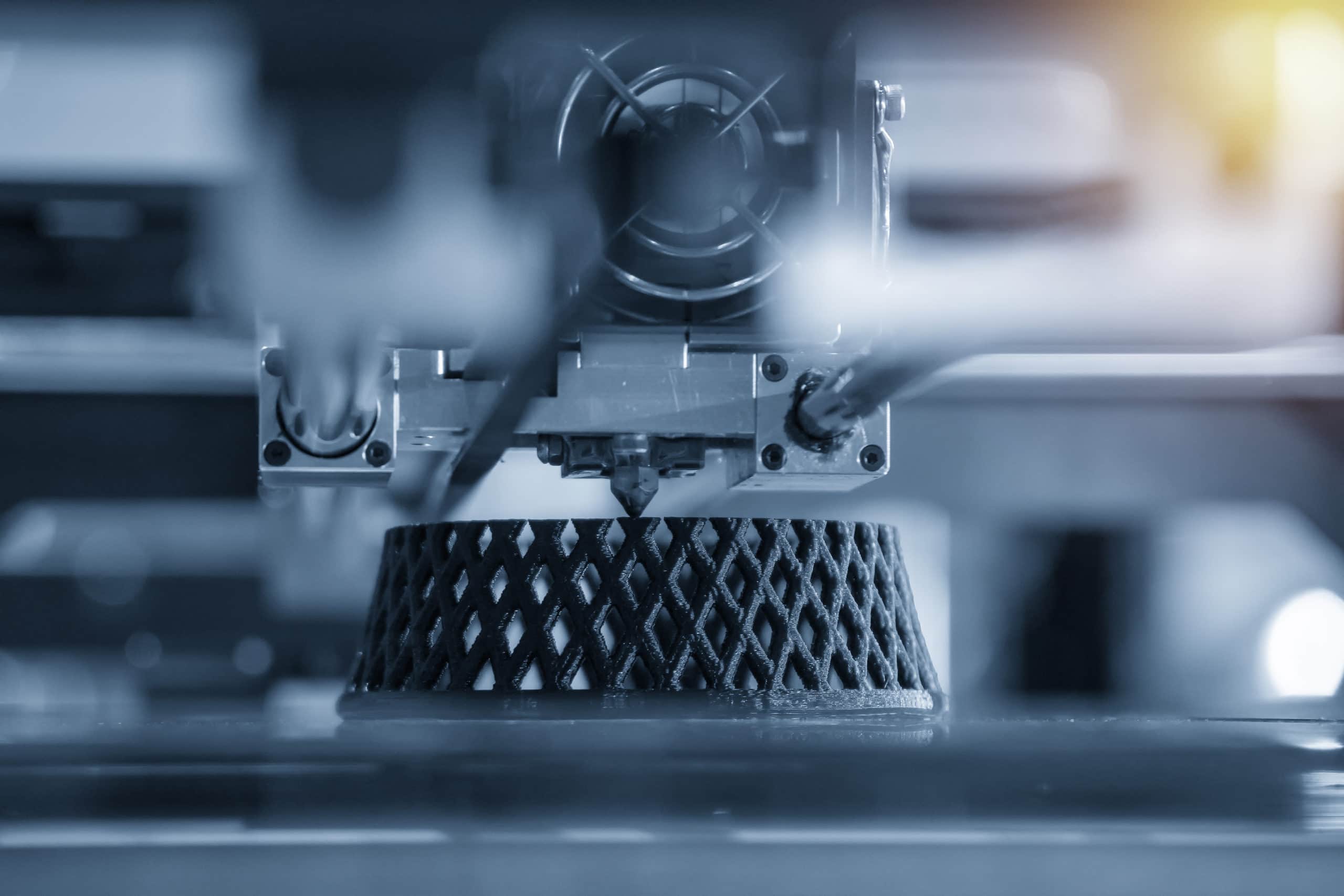
3D printing utilizes a specialized printer and filament material to create the desired object from a digital design file. The printer builds the object by adding successive layers of filament as per the specifications outlined in the file.
Injection molding utilizes pre-made molds to shape material into the desired object. The process involves heating the material to a molten state and then injecting it at high pressures into the mold. After a cooling period, the material is able to maintain the shape of the mold, at which point it is removed and sent for further processing if needed.

Click to Enlarge
While both injection molding and 3D printing can be used for prototyping and production operations, their suitability for a particular project depends on the part and production specifications.
As an additive manufacturing process, 3D printing does not require the use of a mold. Eliminating this tooling requirement benefits manufacturers in many ways. For example:
Given the above, 3D printing is commonly used during the prototyping phase for new parts and products.
One thing to keep in mind regarding 3D printing is that the maximum size of the printed component is limited by the capacity of the print bed. As a result, 3D printed parts and products are generally to under 30”.
As injection molding operations require the use of molds, they generally have longer turnaround times than 3D printing operations since manufacturers need to wait for the mold to be created and delivered. This tooling requirement increases the overall cost of injection molding operations and makes it harder to accommodate design changes. That’s why manufacturers generally use the process for projects involving high production quantities since it lowers per-unit tooling costs.
One thing to keep in mind regarding injection molding is that it can accommodate designs of nearly any size or complexity. Additionally, the molds can be constructed to create multiple units of the same component or different components simultaneously. This capability helps reduce the overall manufacturing time for an order.
Need assistance choosing between 3D printing and injection molding for your next project? Ask the experts at Advanced Prototype Molding! Equipped with over 40 years of experiencing building prototypes and turning them into fully-fledged components, our team has the knowledge and skills to help you determine the right production method for your unique application. Additionally, whether you settle on 3D printing or injection molding, we’re ready to bring your idea to life.
To learn more about our 3D printing and injection molding capabilities, check out our 3D printing and injection molding services pages or contact us today. To discuss your project specifications with one of our team members, request a quote.



ADVANCED PROTOTYPE MOLDING
1520 N Old Rand Road Wauconda, IL 60084
Tel: 847-202-4200
Fax: 847-202-4270
sales@advancedprototype.com

ADVANCED PROTOTYPE MOLDING
1520 N Old Rand Road Wauconda, IL 60084
Tel: 847-202-4200
Fax: 847-202-4270
sales@advancedprototype.com